Quality Marine Refrigeration Systems
A crucial ship component is the marine refrigeration system, which maintains optimal conditions for food, drinks, cargo, and waste. Proper food and beverage storage maintenance is vital to uphold the well-being of passengers and crew. Additionally, given their primary role in safeguarding cargo quality during transport, cargo ships often require top-notch marine refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
Coolblue Marine Refrigeration
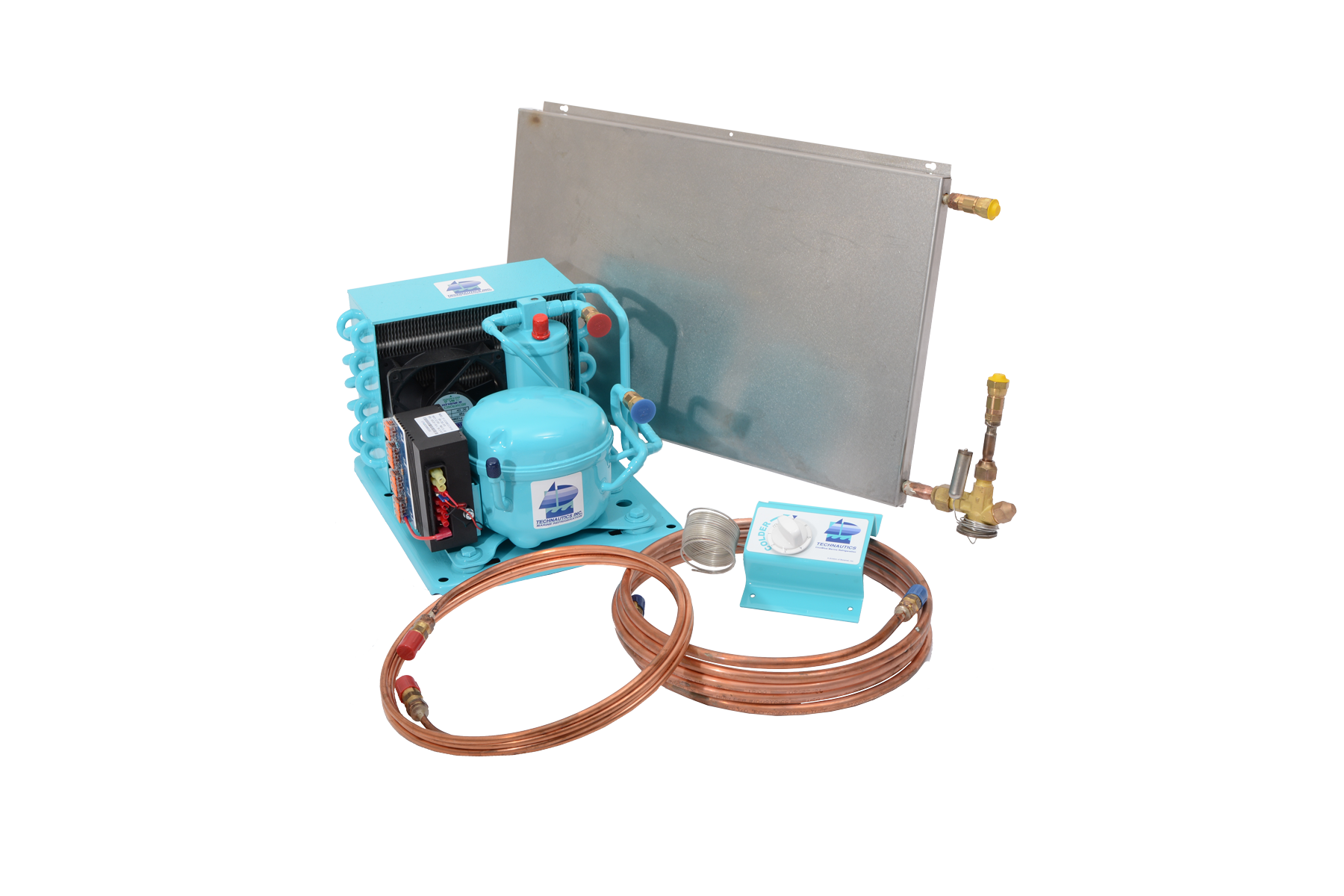

System Evaporator
The System Evaporator is a critical component within the Coolblue Refrigeration system. This integral part ensures efficient and reliable refrigeration performance, contributing to the overall functionality of the marine refrigeration system.
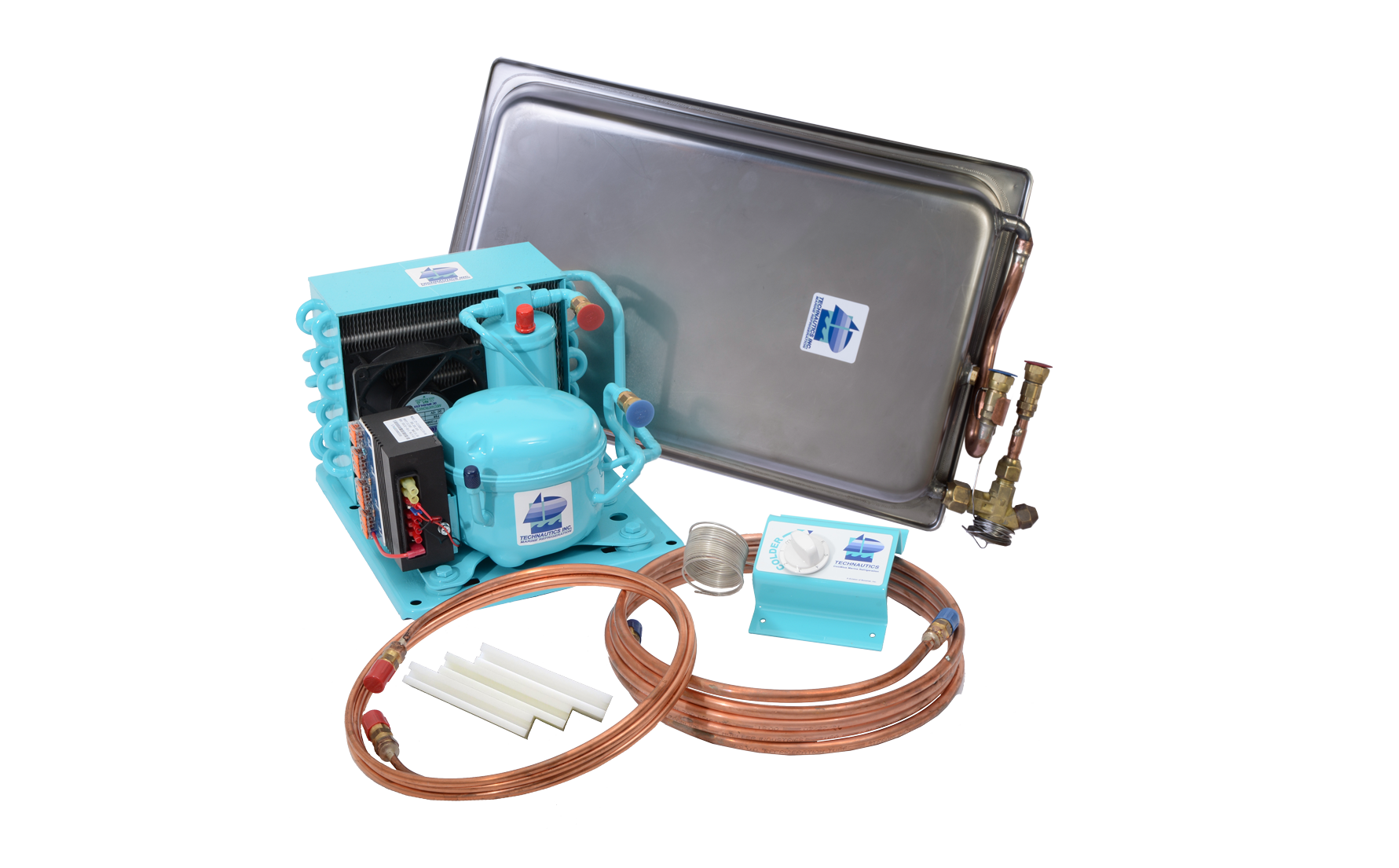

Cooling System
Coolblue Marine Refrigeration incorporates an advanced Cooling System designed to meet the diverse needs of vessels at sea. This system regulates the temperature of perishable goods and contributes to the overall climate control on board.
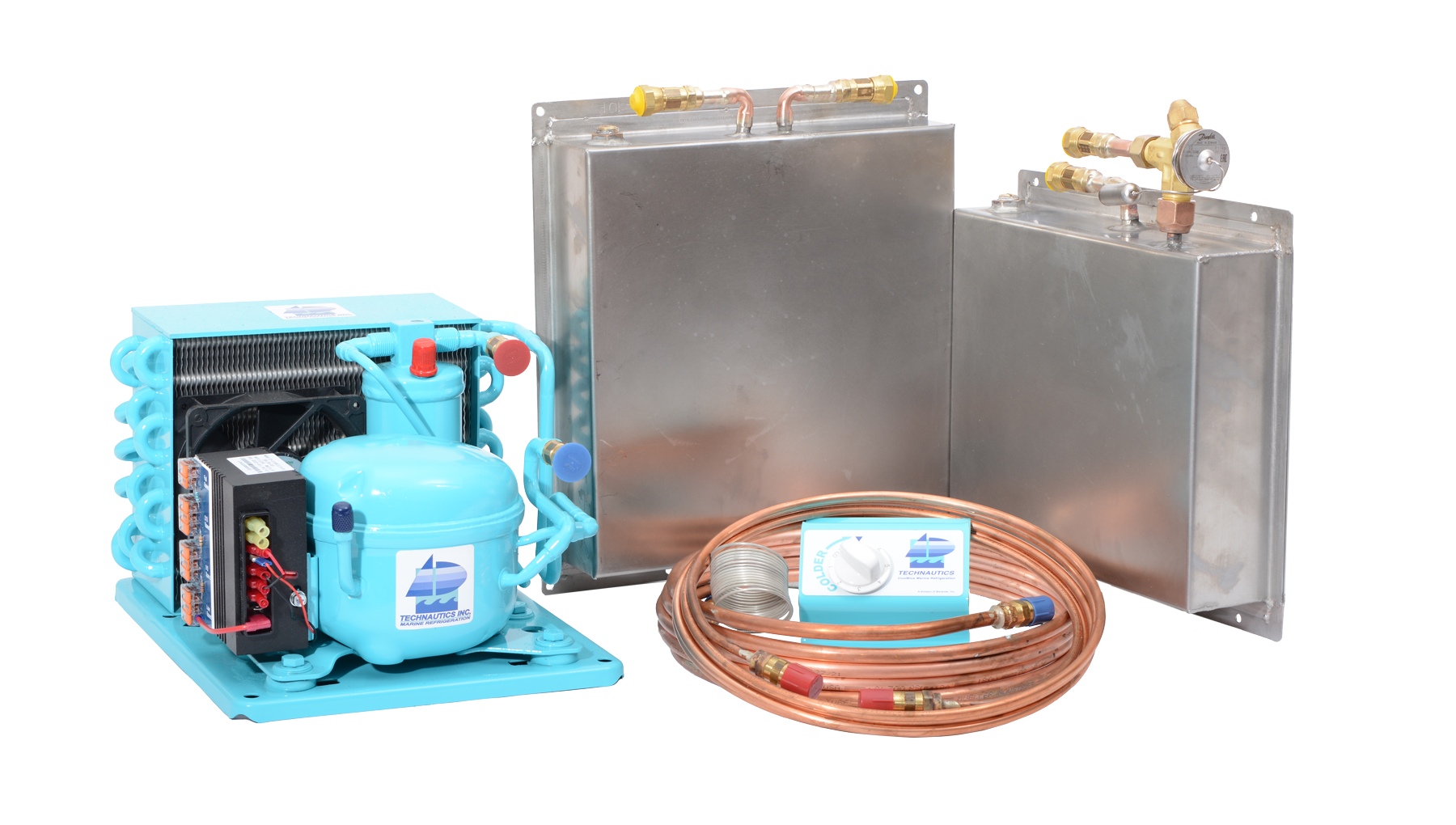

Custom System
For specialized requirements and unique challenges, Coolblue offers a Custom System tailored to the specific needs of individual vessels. With flexibility and precision, Coolblue's Custom System sets a new standard for marine refrigeration customization.
Frigomar USA
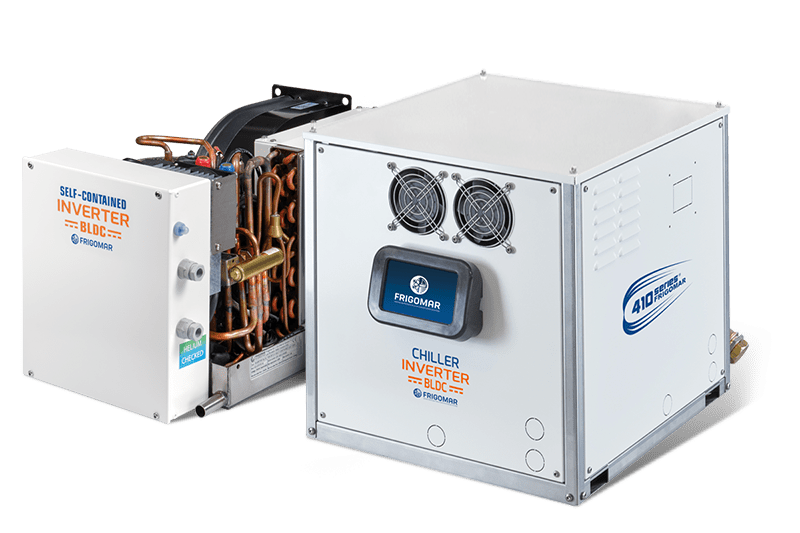

AC Systems
Frigomar USA stands at the forefront of marine climate control with its state-of-the-art AC Systems. Designed to provide comfort and optimal climate conditions on board, these systems are engineered with cutting-edge technology to meet the unique challenges of marine environments.
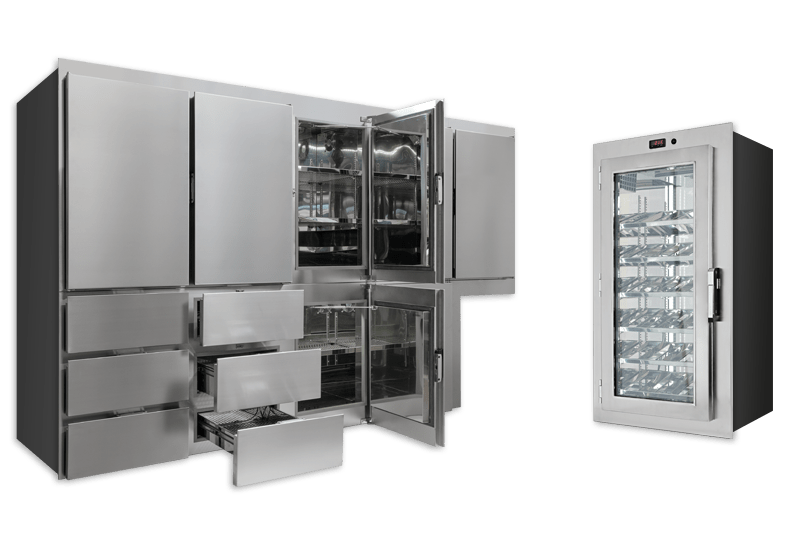

Boat Refrigeration Systems
With a commitment to innovation and reliability, Frigomar's Boat Refrigeration Systems are equipped with advanced features, ensuring that maritime refrigeration needs are met seamlessly. Whether on a small yacht or a larger vessel, Frigomar's solutions provide efficient cooling solutions for maritime applications.
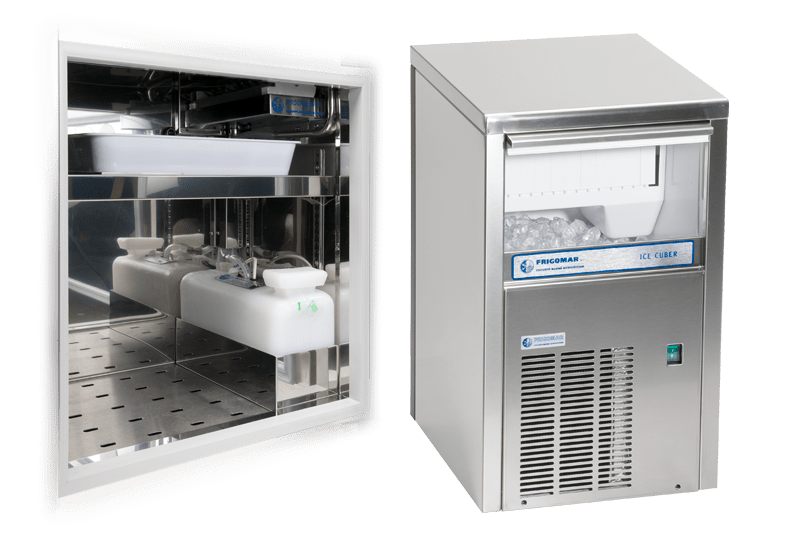
Boat Refrigeration Systems
Frigomar's Ice Making Systems are built with durability and performance in mind, ensuring a consistent and accessible source of ice for various marine applications. Whether for leisure or commercial purposes, these systems contribute to the overall functionality of vessels, enhancing the onboard experience for all.
Upgrades and Accessories

RO System Parts
Cruise RO carries various RO system parts to service and maintain your RO system. Our commitment to quality and durability ensures that every component in our inventory is meticulously crafted to withstand the rigors of the maritime environment.

Marine Refrigeration Parts
Explore our comprehensive selection of marine refrigeration parts, including compressors, condensers, evaporators, thermostats, and more. Whether you are a boat owner, marine technician, or involved in the maritime industry, we understand the critical importance of reliable refrigeration systems on board.

Upgrades
Upgrade your marine RO system today with our quality enhancements and experience a new level of efficiency, reliability, and water purity. Our advanced upgrades address the distinct challenges of marine applications, ensuring your RO system performs exceptionally in any maritime setting.
Why Choose Cruise RO Water and Power?

Experience
With sailing experience and industrial manufacturing expertise, we grasp your cruiser’s necessities. Our RO system reviews indicate we have the know-how to fulfill your needs.

Quality
We offer a range of top-tier products. From boat refrigerator systems to our very own CruiseRO watermakers, our product selection can elevate your maritime experience with our high-quality solutions.

Affordability
Access to drinking water on board is not a luxury; it’s a necessity. Our cost-effective systems feature non-proprietary components, minimizing upfront and replacement expenses.
Adaptability
At CruiseRO, we create custom systems that seamlessly adapt to your unique requirements, ensuring a personalized onboard water supply that perfectly suits your journey.
What Our Customers Are Saying



Questions? We Are Here To Help.
Email or call and talk to the owners of the Company and the Designers, Rich and Charlie, 7 Days-A-Week. If they are awake, they answer!
SALES & TECH SUPPORT
MANUFACTURING & SHIPPING
SKYPE
